Introduction to Mount Rinjani: Indonesia’s Second Highest Volcano
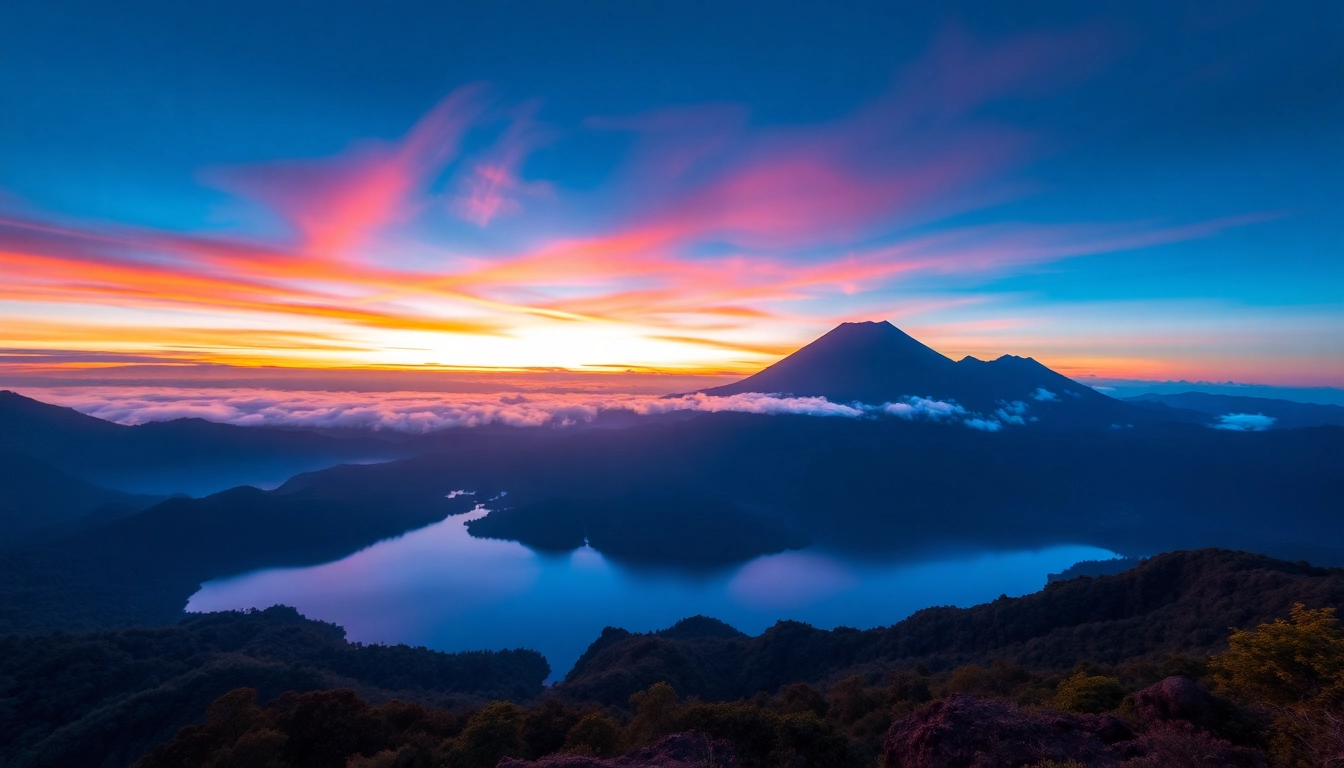
Perched majestically on the island of Lombok in Indonesia, Mount Rinjani is a towering volcano that captures the imagination of adventurers, nature lovers, and culture enthusiasts alike. As the second highest volcano in Indonesia, standing at 3,726 meters (12,224 feet) above sea level, Rinjani’s dynamic landscape and rich history make it a premier destination for trekking, sightseeing, and cultural exploration.
This active volcano has shaped not only the physical landscape of Lombok but also its cultural and ecological fabric. With its recent eruptions and continuous geological activity, Rinjani embodies the raw power of nature while offering a unique opportunity for visitors to witness and experience the resilience of ecosystems and communities that thrive within its vicinity. This comprehensive guide will delve into every aspect of Mount Rinjani—from its geography and history to practical tips for exploration—enabling you to appreciate this natural wonder and plan your adventure effectively.
Geographical Location and Physical Features
Location and Accessibility
Mount Rinjani is situated on the northern part of Lombok, a prominent island in Indonesia’s Nusa Tenggara region. It lies within the boundaries of Rinjani National Park, a protected area covering approximately 41,330 hectares. Access to the mountain is predominantly through two main starting points: Sembalun Lawang to the east and Senaru to the north. Both routes offer distinct perspectives and trekking experiences, with Sembalun known for its grassy slopes and scenic vistas, while Senaru offers lush rainforest paths that lead directly to the crater rim.
Topographical and Geological Features
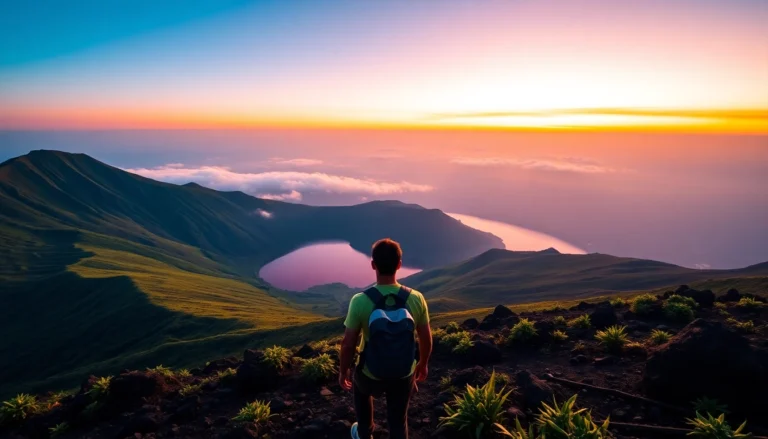
Mount Rinjani is a stratovolcano with a complex silhouette that includes a prominent caldera, a central crater, and multiple volcanic cones. The caldera, measuring about 16 km in diameter, is one of the largest in Southeast Asia, housing the active summit and the iconic Segara Anak Lake—an emerald-colored volcanic crater lake that plays a crucial role in local mythology and ecology.
The volcano features a central crater with an active fumarole system, emitting gases and occasional ash plumes, underscoring its active status. The terrain surrounding Rinjani varies from tropical rainforests at lower altitudes to rugged volcanic rocks, barren slopes, and alpine meadows near the summit. This diverse landscape supports an array of ecosystems, making Rinjani a bio-geographical hotspot.
Climate and Terrain
The region experiences a tropical climate with distinct wet and dry seasons. The dry season, from April to October, offers the best conditions for trekking, characterized by clear skies and minimized rain risk. Terrain-wise, trekkers encounter rocky paths, muddy trails during rainy seasons, and occasionally unpredictable weather—necessitating proper gear and preparation.
Historical Significance and Eruptive History
Mythology and Cultural Importance
Mount Rinjani holds a sacred place in local Sasak and Balinese traditions. It is believed to be the dwelling of spiritual guardians and is central to numerous myths and legends. The lake Segara Anak is considered a divine site, with local communities conducting rituals and ceremonies to honor the mountain’s spirits, seeking blessings for harvests and safety.
Volcanic Activity and Eruptive Patterns
As an active volcano, Rinjani has a long history of eruptions. The most recent significant eruption occurred in 2016, which prompted temporary evacuations and air traffic disruptions. Historically, Rinjani’s eruptions have been characterized by explosive activity, ash and lava flows, and occasional pyroclastic flows, shaping its rugged landscape.
Geologists estimate that Rinjani’s volcanic activity dates back over 100,000 years. Its volcanic history is well documented through ash layers and geological surveys. The volcano’s geothermal activity continues today, with fumaroles, hot springs, and small eruptions serving as reminders of its restless nature.
Historical Impact on Local Communities
Eruptions have periodically impacted nearby villages, affecting agriculture, infrastructure, and livelihoods. Nonetheless, the resilient communities have adapted by integrating the mountain into their cultural identity and sustainable tourism practices, fostering a balance between preservation and exploration.
Natural Landscape and Ecosystems
Flora and Fauna
The ecological tapestry of Rinjani encompasses a wide range of habitats, from tropical rainforests to alpine meadows. The lower slopes are rich with hardwood trees, medicinal plants, and diverse wildlife including the Lombok wren-babbler, ebony bird, and various species of monkeys and deer. As elevation increases, vegetation becomes sparser, giving way to hardy shrubs, grasses, and unique alpine flora.
The park is also home to numerous endemic species, some of which are threatened due to habitat loss and human activity. Conservation efforts focus on protecting these species and restoring degraded habitats.
Water Systems and Geothermal Features
Rinjani’s volcanic activity sustains a network of hot springs, including the famous Aik Berik hot springs near the crater rim, providing a natural relaxation site for trekkers. The crater lake Segara Anak not only adds scenic beauty but also plays a crucial role in the region’s hydrology. Its waters are used by local communities for irrigation and daily needs.
Environmental Conservation and Biodiversity
As a designated national park, Rinjani emphasizes sustainable management. Ongoing efforts include anti-poaching patrols, reforestation projects, and community engagement initiatives aimed at balancing ecological preservation with eco-tourism. Visitors are encouraged to adhere to park guidelines to protect this vulnerable environment.
Top Reasons to Visit Mount Rinjani in Lombok
Exceptional Trekking and Hiking Experiences
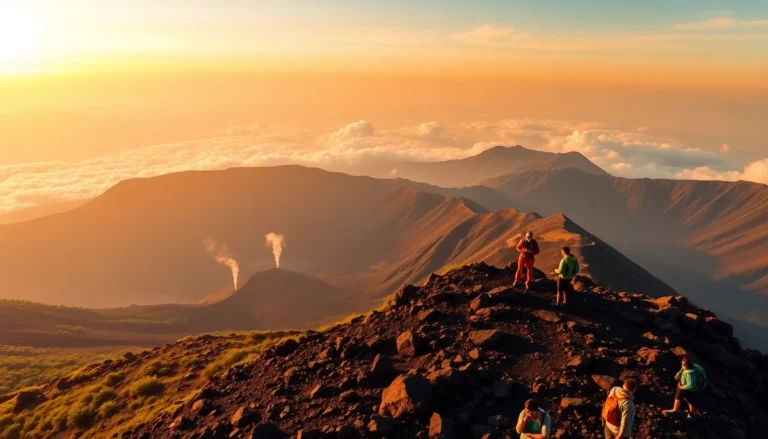
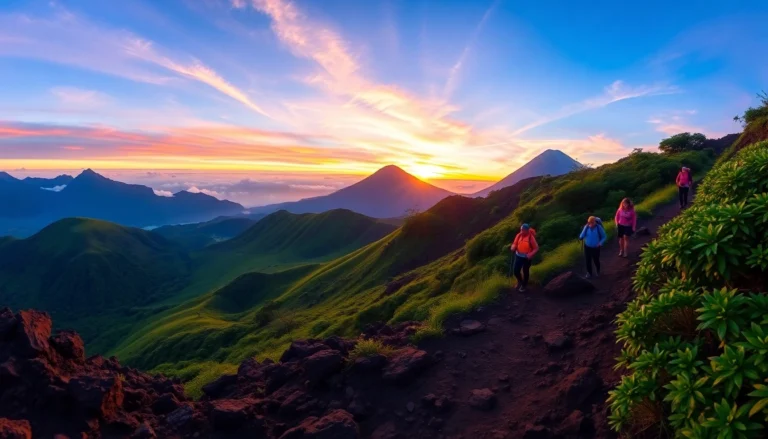
Rinjani offers some of Indonesia’s most challenging and rewarding trekking routes, suitable for experienced hikers as well as adventurous novices. The trail from Sembalun Lawang to the crater rim spans approximately 27 kilometers and typically takes 2-4 days, depending on fitness levels. Trekkers encounter varied terrains—lush forests, volcanic lava fields, and high alpine zones—culminating in breathtaking views from the summit.
Popular trekking routes include:
- Sembalun Route: Known for its scenic grassy slopes and panoramic vistas.
- Senaru Route: Rich in rainforest flora and waterfalls, offering a lush experience.
Guided tours, often including porter and cook services, enhance safety and enjoyment, especially for first-time trekkers.
Unique Natural Attractions Within the National Park
Beyond the summit, Rinjani National Park boasts numerous attractions such as:
- Segara Anak Lake: A serene volcanic crater lake, ideal for relaxing after a trek.
- Rinjani Waterfalls: Including Sendang Gile and Tiu Kelep near Senaru, offering stunning cascades amidst tropical greenery.
- Hot Springs: Like Aik Berik, where visitors can indulge in thermal baths powered by volcanic activity.
Cultural and Local Traditions Around Rinjani
The mountain’s spiritual significance is reflected in vibrant ceremonies and local customs. During certain festivals, local communities perform offerings and rituals to honor the mountain spirits, fostering a deep cultural connection. Visitors can experience unique cultural expressions, traditional dances, and local cuisine in nearby villages, enriching their exploration beyond natural sights.
Guided Trekking and Visitor Tips for Mount Rinjani
Best Seasons and Safety Precautions
The optimal trekking season spans from April to October, coinciding with the dry season, which minimizes weather-related hazards. Trekkers must be prepared for variable weather conditions, including cold temperatures, especially at higher altitudes, and sudden changes in weather patterns. Safety measures include monitoring volcanic activity reports from authorities and being prepared for altitude sickness, dehydration, and hypothermia.
Necessary Equipment and Preparation
Essential gear includes sturdy hiking boots, layers of warm clothing, rain gear, headlamps, and personal essentials like water, high-energy snacks, and a first aid kit. Due to the altitude and terrain, physical training and acclimatization are recommended prior to the trek.
Travel Agencies and Guided Tour Options
Multiple local and international tour operators offer guided packages, including permits, porters, and accommodation arrangements. Hiring experienced guides ensures safety, local insights, and cultural enrichment. Always verify credentials, reviews, and included services before booking.
Environmental Conservation and Sustainable Tourism
Protection of Rinjani’s Ecosystem
To preserve Rinjani’s biodiversity and geological integrity, strict regulations are enforced. Visitors are required to obtain permits, adhere to park guidelines, and avoid activities such as littering, starting fires, or disturbing wildlife. Eco-friendly practices, including waste management and minimal-impact trekking, are promoted to sustain the park’s natural beauty.
Community Engagement and Local Benefits
Local communities benefit significantly from eco-tourism. Initiatives support employment, cultural preservation, and local entrepreneurship, such as homestays and craft markets. Engaging with local guides and artisans ensures that tourism revenues contribute directly to community development.
How Visitors Can Minimize Impact
Visitor responsibilities include practicing the Leave No Trace principles, supporting local businesses, and respecting cultural sites. Staying on designated trails, avoiding single-use plastics, and participating in conservation programs help safeguard Rinjani for future generations.
Planning Your Adventure: Practical Information for Mount Rinjani
Access Points and Transportation
Getting to Mount Rinjani involves flying into Lombok International Airport, followed by land transportation to starting points like Sembalun or Senaru. Local transport options include taxis, motorbikes, or shuttle services arranged through tour providers. From these bases, guided treks or self-guided adventures can commence.
Permits and Entry Requirements
All trekkers require permits issued by the National Park authority, which can be obtained in advance or on arrival. Permits are essential for environmental protection, safety, and regulation. It’s advised to arrange permits through a licensed tour operator to streamline the process.
Accommodation and Facilities Near the Mountain
Options range from simple guesthouses and homestays in Sembalun and Senaru to more comfortable lodges and camping sites within the park. Many trekking packages include overnight stays in designated shelters or tents. Facilities such as food stalls, rest areas, and emergency services are available in surrounding villages and trailheads.
Conclusion: Embrace the Majesty of Mount Rinjani
Mount Rinjani remains an awe-inspiring symbol of Indonesia’s natural and cultural heritage. Its challenging treks, breathtaking landscapes, and spiritual significance offer an unparalleled journey for those willing to embrace its wonders responsibly. With proper preparation, respect for the environment, and an appreciation for local traditions, visitors can experience the profound beauty and resilience of this towering volcano, making their adventure both transformative and memorable.